Introduction
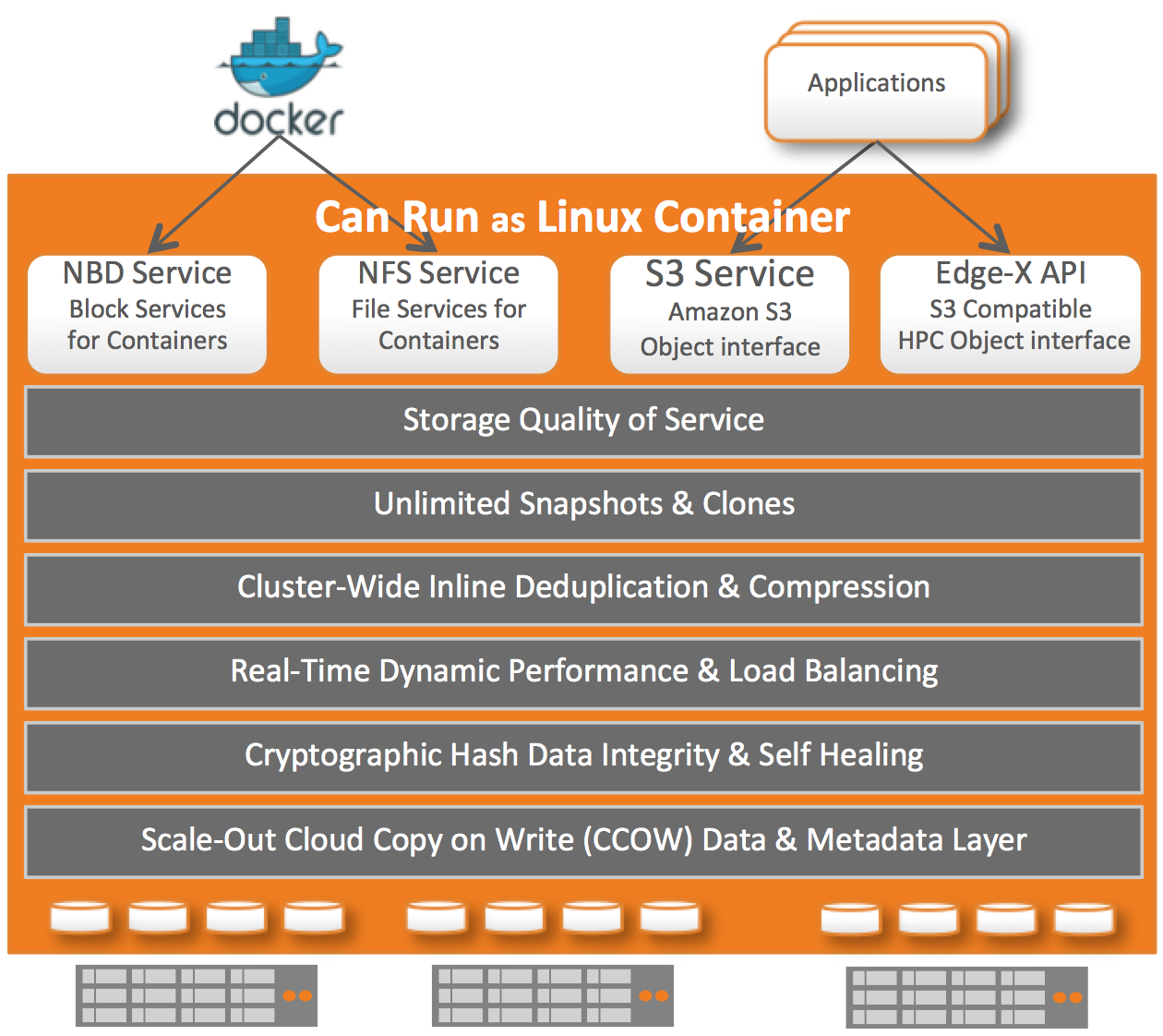
Fast, feature rich and easy to use File, Block and Object storage for your Cloud-Native Applications. It is designed to make use of off the shelf storage and networking infrastructure and present it as enterprise grade SDS (Software-Defined Storage) solution.
NexentaEdge nodes are deployed as containers on physical or virtual hosts, pooling all their storage capacity and presenting it as fully compatible S3/SWIFT object access for containerized applications running on the same or dedicated servers. Additionally data can be accessed as native block devices (NBD), iSCSI (with optional HA), NFS shares (with optional HA) and as High-Performance NOSQL interface. Storage services are managed through standard Docker tools, for greater agility and scalability. Advanced CLI and nice GUI provided for easy of use.
NexentaEdge supported protocols:
- AWS compatible S3 object protocol
- EdgeX-S3 - NexentaEdge specific extensions (RW objects, Snapshots/Clones, NOSQL K/V Database, and more)
- OpenStack SWIFT object protocol
- iSCSI with Active/Passive HA
- NFSv3 with Active/Passive HA and horizontal scalability
- NBD - Native Block Device (no iSCSI overhead, connected directly to Replicast backend network)
CCOW: Technology overview
Architecturally it is software defined clustered object storage solution built upon Cloud Copy on Write (CCOW) idea. Fundamentally it enforces full immutability of any data in the clustered global name space. That is metadata and data are equally made immutable and cannot be modified. Visually it can be presented as classic immutable binary trees data structure managing references to "chunks". In CCOW objects split down into one or more chunks. Those chunks are immutable (“copy-on- write”), and their locations are not stored in the metadata. CCOW supports two types of object payload: an array of bytes and arrays of key/value records. File systems have long distinguished between data and metadata. CCOW stores metadata in Manifest Chunks, and data in Payload Chunks. Both are chunks, with nearly identical operations and characteristics.
With CCOW data format technology provides differentiating capabilities:
guarantee of total and complete immutability of both Data and Metadata. Users data never gets overwritten and this creates number of advantages among which best in class data consistency and reliability
transparent bi-directional (upcoming feature) synchronization between multiple data-centers and clouds (Object interfaces only)
unique on-demand fetching technique and metadata only synchronization where only needed portions of object has to be fetched from the remote site (upcoming feature)
global metadata indexing and search with Elastic framework
embedded audit trails and rule based policy engine
end-to-end data integrity, resilience to networking splits and partial cluster availabilities. Data can be transported over long distances without loosing its original consistency
data (object, files and block volumes) and metadata stored as variable sized chunks, from 8KB to multi MB size chunks depending on I/O pattern requirements for the data access
cryptographic hash on all chunks stored in the cluster and no need for periodic scrubbing. Data is always consistent
immutable chunks simplify efficient multi-level caching throughout the scale-out cluster. Performance acceleration without the need for complex cache invalidation logic
local access point acceleration (network transfers avoidance). Application gateways can access locally provisioned storage, which can still be part of much larger global cluster name space
FlexHash and Replicast: Technology overview
NexentaEdge is scale-out distributed clustered system of connected servers (nodes). Logically nodes can have designated data storage role, designated gateway role or combination of both roles (mixed). Nodes connected together via Ethernet fabric using low latency and high-performance UDP-based protocol called Replicast. While distribution of chunks is managed via directing hashing table called FlexHash. FlexHash dynamically organizing and assigns all disks into appropriate so-called "Negotiating Group". Negotiating Group is group of disks distributed across physical servers and racks in accordance with selected policy (server or zone). FlexHash technology solves data placement challenges of consistent hashing. It dynamically places data based on utilization and rebalances resources automatically. Utilizing a dynamic, decentralized hash table allows NexentaEdge to scale to virtually unlimited size.
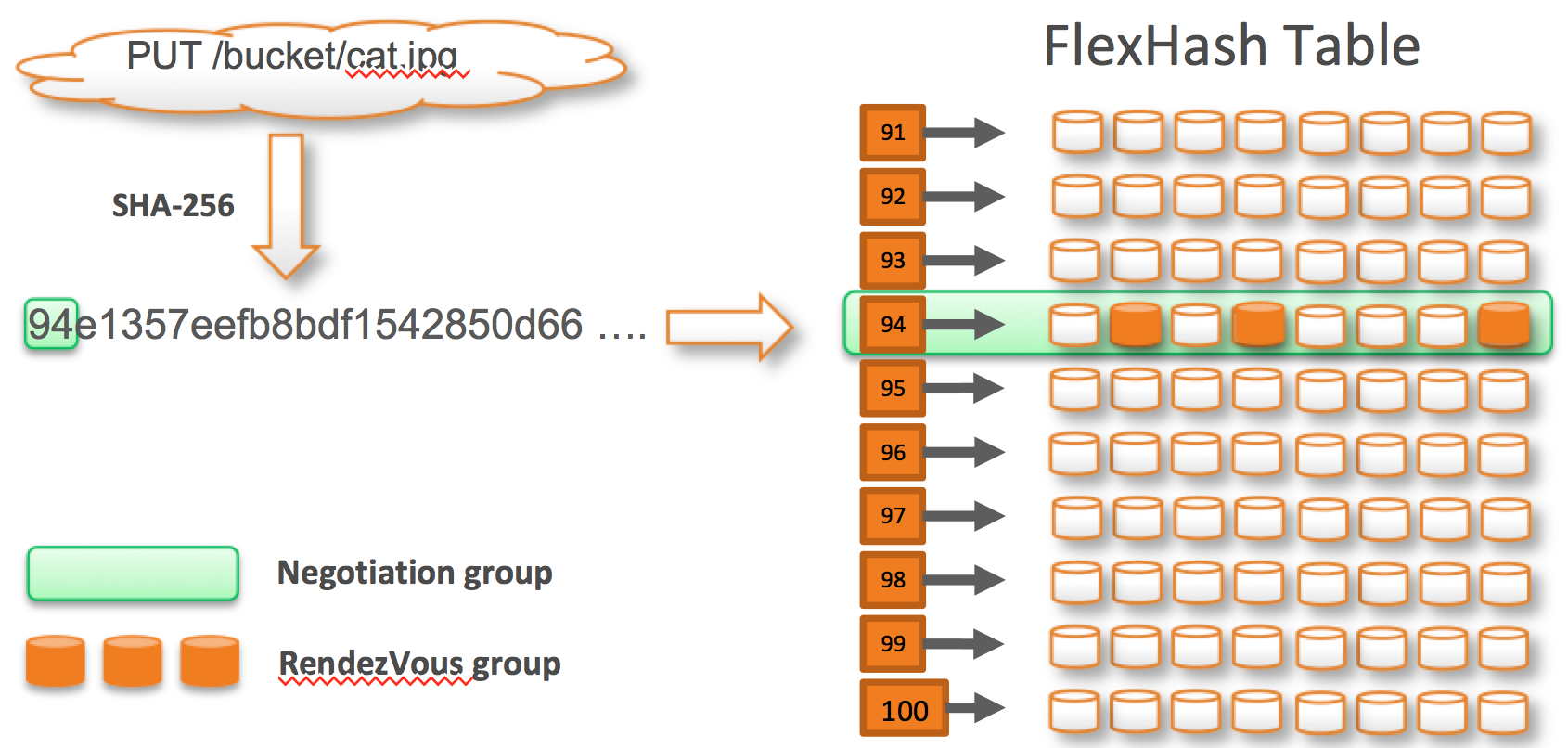
In the diagram above, the name of the Object is used to generate a digest using SHA-256. This digest is the starting point for named objects. For individual data chunks a content digest is used. The digest is used to look up a negotiation group of storage devices. Real time negotiation with members of Negotiation group using Replicast identifies the best number of replica target devices to use to store the object chunk based on utilization, latency or both policy.
FlexHash and Replicast provide failure resilient, high-performance and dynamic data placement with inline data-deduplication, high accuracy I/O load balancing, high-performance UDP-based transfers. Differentiating benefits can be summarized as:
content addressable placement of data within a Negotiating Group. Not a consistent hash ring, improved operational efficiencies of rebalance/join/leave
dynamic negotiation of the “best device” to store data within that group. “Best” is a function of available device capacity, response time and queue depth, achieve close to 100% device utilization
no need to transfer data chunk if hash already exists in a Negotiating Group. A.K.A. Deduplication technique
transparent handling of hardware failures = Data flows around failures. A server failure simply reduces the number of candidate devices in a Negotiating Group. No need to ever “fail-back” data to a pre-determined location. It only needs to be in the right Negotiating Group. Great for seamless handling of network hiccups, or server reboots, or server maintenance operations
microsecond-level resolution data transfer protocol, using Ethernet and L3/UDP. Cost savings in achieving same or similar transfer speeds then with specialized hardware (RDMA/IB)
standard feature set of reliable storage transport with minimal overhead. Packets handled in user space, zero copy whenever possible and low latency processing
reliable delivery with “optional” Multi-cast Rendezvous Transfer. Write I/O san be up to 300% faster to transfer 3 replicas on the same networking port
Replicast transport protocol is responsible for low latency and high throughput communications and supports the following modes of operation:
UDP/IP Unicast (Cloud option) or Multicast communications within Negotiating Group
UDP/IP Unicast or Multicast communications within Rendezvous Transfer Group (group selected targeted devices)
TCP/IP communications within Rendezvous Transfer Group (Cloud option)
Accelerated PF_RING Rendezvous Transfer (aka DPDK-like based) or low CPU overhead option (upcoming feature)
By default NexentaEdge installs in two configurations as far as Replicast transport protocol is concerned:
Data Center option: with UDP/IP for Multicast in Negotiating Groups and UDP/IP Unicast for Rendezvous Transfers
Cloud option: with UDP/IP or TCP/IP Unicast only transport
